Video Archive
- From Around the Web, Science & Technology
- September 19, 2017
Structural ‘supraball’ pigments could transform cosmetics and food.
READ MORE
- From Around the Web, Space
- May 18, 2021
If asked where meteorites come from, you might reply “from comets.” But according to our new research, which tracked hundreds of fireballs on their journey through the Australian skies, you would be wrong.
READ MORE
- From Around the Web, UFO News
- September 16, 2017
Documentary on a case in Brazil where people claim to have been attacked by aliens and others killed by them.
READ MORE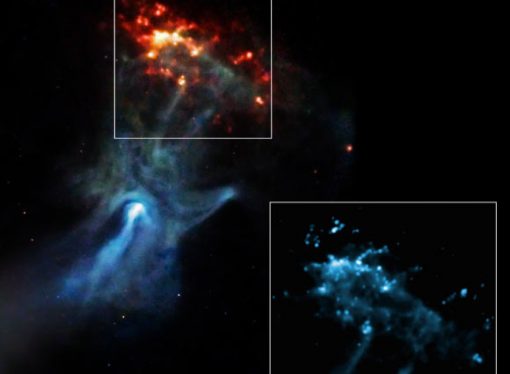
- From Around the Web, Space
- June 25, 2021
A stellar structure known as the ‘Hand of God’ is a nebula of energy and particles blown by a pulsar left behind after a star exploded in our Milky Way Galaxy. Otherwise known as MSH 15-52 or G320.4-1.2, the object is located some 17,000 light-years away in the constellation of Circinus. Astronomers estimate that light from the supernova explosion reached Earth about 1,700 years ago, or when the Mayan empire was flourishing and the Jin dynasty ruled China. Previously, astronomers had released a full view of the structure. In a paper in the Astrophysical Journal Letters, they report how quickly the supernova remnant associated with the hand is moving, as it strikes a cloud of gas called RCW 89; the inner edge of this cloud forms a gas wall located about 35 light-years from the center of the explosion.
READ MORE

- From Around the Web, Space
- April 26, 2021
Monday, NASA’s Ingenuity Mars Helicopter became the first aircraft in history to make a powered, controlled flight on another planet. The Ingenuity team at the agency’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California confirmed the flight succeeded after receiving data from the helicopter via NASA’s Perseverance Mars rover at 6:46 a.m. EDT (3:46 a.m. PDT).
READ MORE
- From Around the Web, Space
- December 5, 2020
The giant radio telescope had special features that aren’t easily replaced
READ MORE
