Superfast star found leaving Milky Way at 1,700km per second0
- From Around the Web, Space
- November 13, 2019
Astronomers say S5-HVs1 ventured close to supermassive black hole before being ejected

Astronomers say S5-HVs1 ventured close to supermassive black hole before being ejected
An international team of astronomers has discovered a massive cloud of gas that formed just 850 million years after the Big Bang. The chemical composition of the object reveals that the first generation of stars formed quickly and enriched the Universe with the elements they synthesized.

Astronomers know that most galaxies house supermassive black holes in their centers, from the largest galaxies down to small dwarfs.

New method used to study planets’ geochemistry implies that Earth is not unique

Astronomers have gotten the earliest look yet at a tidal disruption event

A team of astrophysicists from Columbia University proposes that the strange long-term dimming of the KIC 8462852 star (also known as Tabby’s star or Boyajian’s star) is the result of a disk of debris — torn from a melting moon – that is accumulating and orbiting the star.

Astronomers have discovered the most massive neutron star to date, a rapidly spinning pulsar approximately 4,600 light-years from Earth. This record-breaking object is teetering on the edge of existence, approaching the theoretical maximum mass possible for a neutron star.
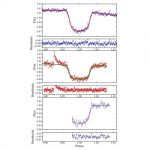
An international team of astronomers has detected a new brown dwarf with an ultra-short orbital period that transits an active M-dwarf star. The newfound object, designated NGTS-7Ab, turns out to be the shortest period transiting brown dwarf around a main or pre-main sequence star discovered to date. The finding is detailed in a paper published June 19 on the arXiv pre-print server.

The finding suggests the outburst of stellar energy are more common than scientists thought
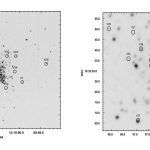
Using the Devasthal optical telescope in India, astronomers have conducted photometric observations of the globular cluster NGC 4147. The observational campaign yielded the discovery of 28 new variable stars in this cluster. The findings are detailed in a paper published May 20 on the arXiv pre-print server.