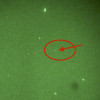
There’s a planet exactly where Star Trek said Vulcan should be0
- From Around the Web, Space
- September 21, 2018
Countdown: 45 years left until ‘First Contact’

Countdown: 45 years left until ‘First Contact’

Physicists build giant machines to study tiny particles

NASA’s New Horizons spacecraft has made its first detection of its next target, the Kuiper Belt object 2014 MU69, more than four months ahead of its 2019 close encounter.

European Space Agency’s seven-year, €1bn mission will investigate the effects of the sun on satellite technology

Pi Men c’s size and mass suggest it may have lots of water

After an almost two-year journey through space, NASA’s Origins, Spectral Interpretation, Resource Identification, Security-Regolith Explorer (OSIRIS-REx) caught its first glimpse of Bennu, a carbonaceous asteroid whose makeup may record the earliest history of our Solar System, last week and began the final approach toward the asteroid. Using its multipurpose PolyCam camera, the spacecraft obtained the image of Bennu from a distance of 1.4 million miles (2.2 million km), or almost six times the distance between the Earth and Moon.

Changing how the skins wrap around a tube can achieve different types of motion

We usually associate volcanoes with extreme heat. But new results demonstrate that the Solar System’s largest asteroid, Ceres, is covered in volcanoes that have spewed ice throughout their history.

Thanks to Plato’s account of the lost city and Google Earth, new visual and arithmetic clues suggest that the mythical city of Atlantis may have been hiding in plain sight the entire time, in rather an unlikely place.

Force of light boosts electrons close to speed of light