NorthStar satellite system to monitor threat of space debris0
- From Around the Web, Science & Technology, Space
- October 31, 2020
Space-based service will alert users to potential collisions between satellites and orbital junk

Space-based service will alert users to potential collisions between satellites and orbital junk
NASA’s Juno spacecraft has been in orbit around Jupiter since 2016. One of its instruments is the ultraviolet spectrograph (UVS), which is primarily used to make ultraviolet images of Jupiter’s auroras. During the first four years of the mission, the UVS instrument has observed 11 transient bright flashes. These flashes look similar to lightning, but are located much higher in the atmosphere than the cloudy regions of Jupiter where lightning is generated. In a paper published in the Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets, researchers suggest that these are observations of transient luminous events in the gas giant’s upper atmosphere. In particular, they suggest that these events are elves, sprites or sprite halos, three types of transient luminous events that produce spectacular flashes of light very high in the Earth’s atmosphere in response to lightning strikes between clouds or between clouds and the ground.

How likely you are to trust a self-driving car or advice from Siri?

The wealth is out there.

The company provided the bunker’s coordinates, just in case

The rover is taking a curved route due to the Sun’s gravitational pull

Astronomers have discovered a planetary free agent floating through the Milky Way, unbound to the gravity of any nearby stars. The discovery, detailed Thursday in Astrophysical Journal Letters, suggests the Milky Way may be teeming with rogue planets.
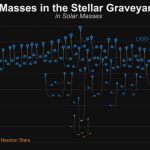
The LIGO Scientific Collaboration and Virgo Collaboration released a catalog of results from the first half of its third observing run (O3a), and scientists have detected more than three times as many gravitational waves than the first two runs combined.

A University of Hawaiʻi Institute for Astronomy (IfA) astronomer has revealed critical new findings linked to a large asteroid expected to pass extremely close to Earth.

Astronomers get to the heart of the Milky Way.



