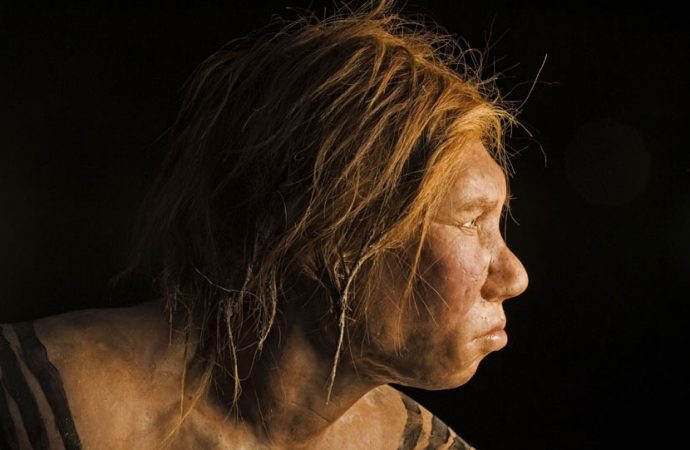
When our ancestors first migrated out of Africa around 60,000 years ago, they were not alone. At that time, at least two other species of hominid cousins walked the Eurasian landmass—Neanderthals and Denisovans.
As our modern human ancestors migrated through Eurasia, they encountered the Neanderthals and interbred. Because of this, a small amount of Neanderthal DNA was introduced into the modern human gene pool.
Everyone living outside of Africa today has a small amount of Neanderthal in them, carried as a living relic of these ancient encounters. A team of scientists comparing the full genomes of the two species concluded that most Europeans and Asians have between 1 to 2 percent Neanderthal DNA. Indigenous sub-Saharan Africans have none, or very little Neanderthal DNA because their ancestors did not migrate through Eurasia.
On one level, it’s not surprising that modern humans were able to interbreed with their close cousins. According to one theory, Neanderthals, Denisovans, and all modern humans are all descended from the ancient human Homo heidelbergensis. Between 300,000 to 400,000 years ago, an ancestral group of H. heidelbergensis left Africa and then split shortly after. One branch ventured northwestward into West Asia and Europe and became the Neanderthals. The other branch moved east, becoming Denisovans. By 130,000 years ago H. heidelbergensis in Africa had become Homo sapiens. Our modern human ancestors did not begin their own exodus from Africa until about 60,000 years ago, when they expanded into Eurasia and encountered their ancient cousins.
The revelation that our ancient ancestors mated with one another could help explain one of the great mysteries in anthropology: Why did the Neanderthals disappear? After first venturing out of Africa, Neanderthals thrived in Europe for several hundred thousand years. But they mysteriously died out about 30,000 years ago, roughly around the same time that modern humans arrived in Europe.
Some scientists have suggested modern humans out-competed or outright killed the Neanderthals. But the new genetic evidence provides support for another theory: Perhaps our ancestors made love, not war, with their European cousins, and the Neanderthal lineage disappeared because it was absorbed into the much larger human population.
Even though Neanderthals and Denisovans are both extinct, modern humanity may owe them a debt of gratitude. A 2011 study by Stanford University researchers concluded that many of us carry ancient variants of immune system genes involved in destroying pathogens that arose after we left Africa. One possibility is that these gene variants came from other archaic humans.
Source: National Geographic




























Leave a Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.