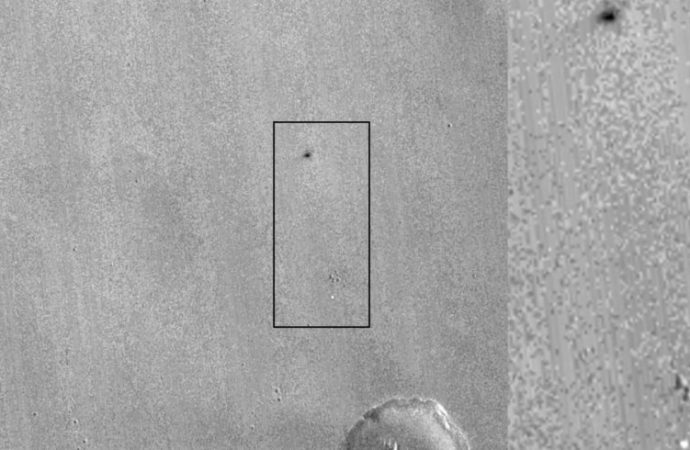
Pictures taken by a NASA satellite show a black spot where the Schiaparelli lander was meant to touch down Wednesday.
Scientists say Europe’s experimental Mars probe has hit the right spot but may have been destroyed in a fiery ball of rocket fuel because it was traveling too fast.
Pictures taken by a NASA satellite show a black spot where the Schiaparelli lander was meant to touch down Wednesday, the European Space Agency said. The images end days of speculation over the probe’s likely fate following unexpected radio silence less than a minute before the planned landing.
The agency said in a statement that the probe dropped from a height of 2 to 4 kilometers (1.4 miles to 2.4 miles) and struck the surface at a speed exceeding 300 kph (186 mph), “therefore impacting at a considerable speed.”
It said the large disturbance captured in the NASA photographs may have been caused by the probe’s steep crash-landing, which would have sprayed matter around like a blast site on Earth.
“It is also possible that the lander exploded on impact, as its thruster propellant tanks were likely still full,” the agency said.
Schiaparelli was designed to test technology for a more ambitious European Mars landing in 2020. The European Space Agency said the probe’s mother ship was successfully placed into orbit Wednesday and soon will begin analyzing the Martian atmosphere in search for evidence of life.
“In my heart, of course I’m sad that we couldn’t land softly on the surface of Mars,” agency chief Jan Woerner told The Associated Press. “But the main part of the mission is the science that will be done by the orbiter.”
Woerner said engineers received a wealth of data from the lander before the crash that will prove valuable for the next attempt in four years. He described the mission as “a 96 percent success.”
Still, the crash-landing was a painful reminder of how hard it is to put a spacecraft on the surface of the red planet.
Its resting place was photographed by NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter , which also spotted Europe’s last ill-fated mission to the surface of the planet. The Beagle 2 probe landed on Mars in 2003 but failed to deploy its solar panels properly, preventing it from functioning.
There have been only seven successful robotic landings on Mars, all by NASA. The last landing was in 2012, when the Curiosity rover touched down in a crater.
Landing on Mars is notoriously difficult because of the planet’s thin, dusty atmosphere. Inbound spacecraft hit the atmosphere at 12,000 mph (19,300 kph) and have only minutes to slow down and land.
With the loss of Schiaparelli, only two spacecraft are currently roaming the Martian surface: Curiosity and Opportunity, which landed in 2004.
The European Space Agency said that, according to what its scientists have been able to piece together so far, Schiaparelli suffered problems during the last 50 seconds of its descent through the harsh atmosphere.
The picture taken by NASA’s orbiter shows two features that weren’t visible on the surface when the spacecraft photographed the area in May. The first is a bright spot of about 12 meters (39 feet) in diameter. The agency says that’s likely to be Schiaparelli’s parachute.
The second feature was described as “a fuzzy dark patch roughly 15 by 40 meters in size” north of the parachute. That’s likely to be the lander.
“These preliminary interpretations will be refined following further analysis” and a high-resolution picture in the coming days, the agency said.
While Schiaparelli was able to beam back some 600 megabytes of data before the crash, scientists won’t get any of the close-up photos the probe took during its descent. Those were meant to be transmitted after the landing.
ESA said the other part of the ExoMars mission — the Trace Gas Orbiter — was “working very well and will take science calibration data during two orbits in November.”
The spacecraft then is supposed to descend to an altitude of about 400 kilometers (250 miles) and begin its study of Mars next year. The orbiter will act as a radio relay for the next stage of the ExoMars mission and future attempts to land on the planet.
Source: Popular Mechanics



























Leave a Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.