Toxoplasma gondii can mess with all sorts of mice behaviors, a new study shows
Source: Science News
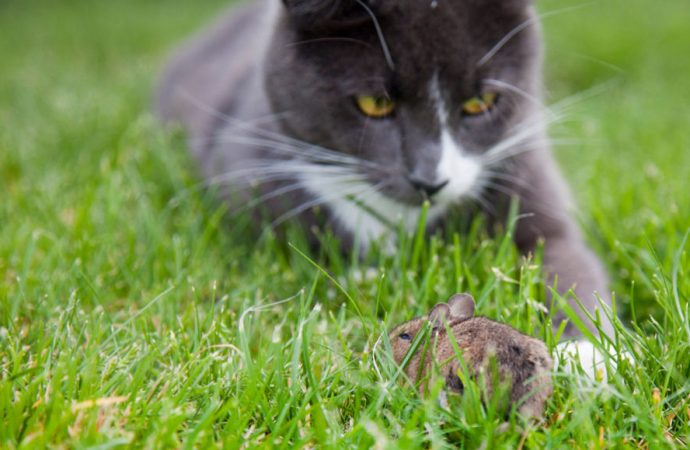
A parasite common in cats can eliminate infected mice’s fear of felines — a brain hijack that leads to a potentially fatal attraction. But this cat-related boldness isn’t the whole story.
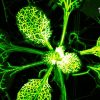
Once in the brain, the single-celled parasite Toxoplasma gondii makes mice reckless in all sorts of dangerous scenarios, researchers write January 14 in Cell Reports. Infected mice spent more time in areas that were out in the open, exposed places that uninfected mice usually avoid.
Infected mice also prodded an experimenter’s hand inside a cage — an intrusion that drove uninfected mice to the other side of the cage. T. gondii–infected mice were even unfazed by an anesthetized rat, a mouse predator, the researchers from the University of Geneva and colleagues found. And infected mice spent more time than uninfected mice exploring the scents of foxes and relatively harmless guinea pigs.
The extent of mice’s infections, measured by the load of parasite cysts in the brain, seemed to track with the behavior changes, the researchers report.
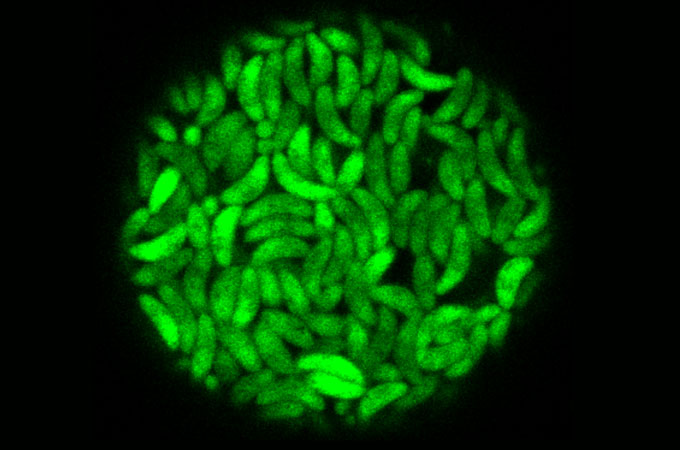
The parasite needs to get into the guts of cats to sexually reproduce. Other animals can become infected by ingesting T. gondii through direct or indirect contact with cat feces. The parasite can then spread throughout the body and ultimately form cysts in the brain.
People can become infected with T. gondii, though usually not as severely as mice. Some studies have hinted, however, at links between the parasite and human behaviors such as inattention and suicide, as well as mental disorders such as schizophrenia.
Source: Science News




























Leave a Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.