The coating flouts the typical trend of hotter objects radiating more light
Source: Science News
Hotter objects typically glow brighter than cooler ones, making them stand out in infrared images. But a newly designed coating bucks the rule that hotter equals brighter. For certain wavelengths of infrared light, the material’s brightness doesn’t change as it warms, researchers report December 17 in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Made of samarium nickel oxide, the thin coating “hides temperature information of surfaces from infrared cameras,” and could therefore be used as a privacy shield, says applied physicist Mikhail Kats of the University of Wisconsin–Madison.
A basic rule of physics known as the Stefan-Boltzmann law states that the brightness of the thermal radiation emitted by an object grows rapidly with increasing temperature. Turn up the heat on an electric stove, for example, and the coils get brighter. The same trend goes for invisible wavelengths of light, such as infrared. Infrared cameras measure how much thermal radiation objects emit in infrared wavelengths to estimate their temperatures. So if the normal link between temperature and radiation is broken, the camera can be fooled.
Samarium nickel oxide doesn’t flout the Stefan-Boltzmann law. Instead, the material’s increasing brightness at higher temperatures is counteracted by a decrease in its emissivity — the tendency to emit thermal radiation. That decrease occurs due to the material switching from an insulator to a metal. The two effects balance out so that, for certain infrared wavelengths, the material’s brightness remains constant as its temperature changes, Kats and his colleagues found.
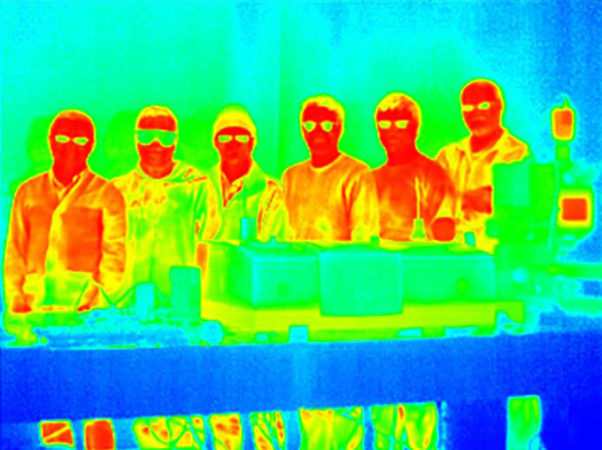

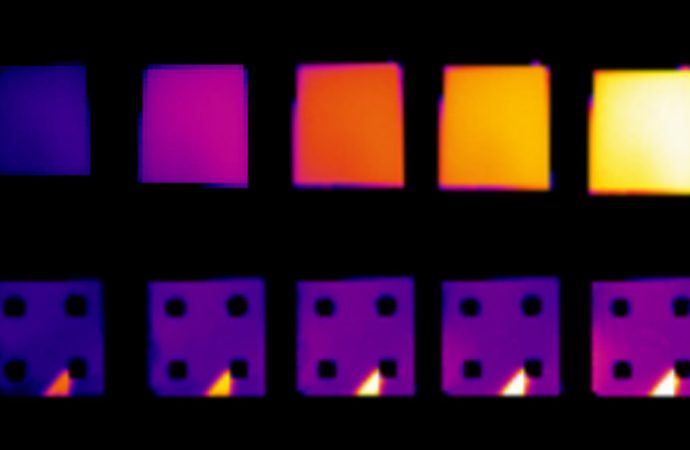
Earlier research has pinpointed substances that could confuse infrared cameras by appearing cooler as their temperatures rise. But the new material achieves a sweet spot where the material’s temperature can rise or fall with little sign of the temperature difference showing up in infrared images. In experiments, the researchers heated a sapphire sample coated with the material, and its temperature in infrared images appeared mostly unchanged from around 105° to 135° Celsius.
“The phenomenon is quite interesting” says physicist Karl Joulain of the University of Poitiers in France. But current applications of the material are “quite limited,” he says. The effect applies only to certain infrared wavelengths. Detectors that look at other wavelengths could still spot an object’s change in temperature.
Still, with infrared devices becoming cheaper and more common, “that comes with quite a bit of privacy implications,” Kats says. The cameras can be used to search unwitting subjects for medical conditions, for instance, or to detect sources of heat behind thin walls.
For now, the high temperatures at which the camouflage effect occurs means it wouldn’t be useful for concealing people. However, Kats thinks the temperature range can be changed by working with alloys of samarium nickel oxide, which may have different properties.
Source: Science News




























Leave a Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.