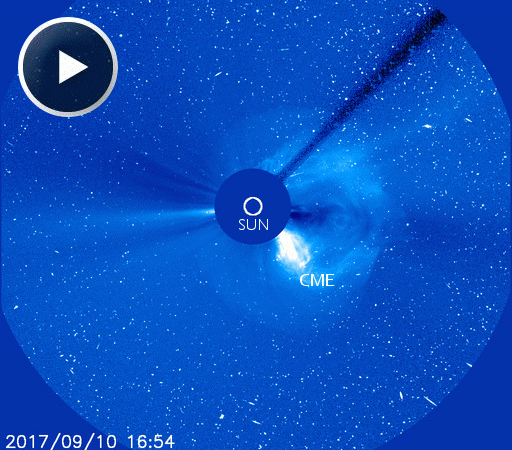
On Sept. 10th, departing sunspot AR2673 erupted, producing a powerful X8-class solar flare. The explosion propelled a CME into space and accelerated a swarm of energetic protons toward Earth. Both are visible in this coronagraph movie from the Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO): The many specks in this movie are not stars–they are solar protons
On Sept. 10th, departing sunspot AR2673 erupted, producing a powerful X8-class solar flare. The explosion propelled a CME into space and accelerated a swarm of energetic protons toward Earth. Both are visible in this coronagraph movie from the Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO):
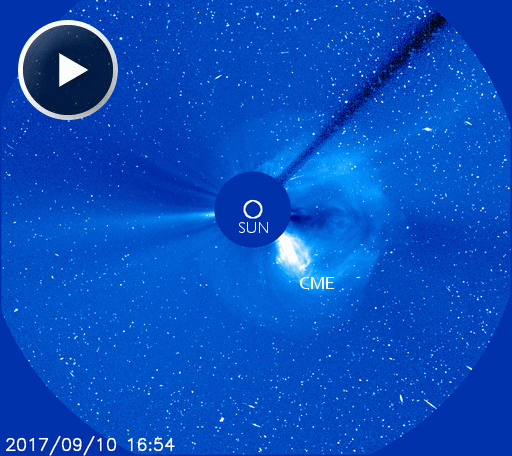
The many specks in this movie are not stars–they are solar protons striking SOHO’s digital camera. Almost two days later these protons are still streaming past our planet, causing a moderately strong (S2-class) solar radiation storm. The latest data from SOHO show an ongoing blizzard of digital “snow” in coronagraph images:

What made this flare so ‘radioactive’? It has to do with the location of AR2673 at the time of the explosion. The sun’s western limb is magnetically well-connected to Earth. Look at this diagram. Magnetic fields spiraling back from the blast site led directly to our planet, funneling these energetic protons Earthward.
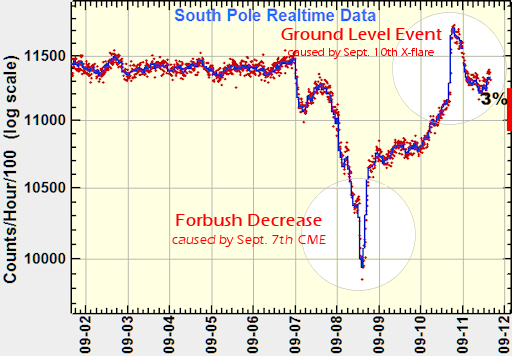
Normally, solar radiation storms are held at bay by our planet’s magnetic field and upper atmosphere. On Sept.10th, however, there was a “ground level event” (GLE). Neutron monitors in the Arctic, Antarctic, and several other high latitude locations detected a surge of particles reaching all the way down to Earth’s surface:
 :
:
The Bartol Research Institute’s South Pole Neutron Monitor detected a GLE on Sept. 10th.
“”In historical terms, this was a relatively small ground level event– only about one thousandth as strong as the event of 23 Feb 1956, which is the largest measured,” says Clive Dyer, a Visiting Professor at the University of Surrey Space Centre.
However, that does not mean the Sept.10th GLE was negligible. Dyer says that “passengers flying on high-latitude routes at 40,000 feet could have absorbed an extra 10 microSieverts of radiation. During the first hour of the GLE, the dose rate inside the aircraft during such a flight would have approximately doubled.”
He also notes that the GLE could have caused minor upsets of onboard electronics and avionics, although nothing on the scale of the epic 1956 GLE, “which would be very challenging to modern systems.”
“Since measurements began around 1942 there have now been 73 events detected by ground level radiation monitors,” Dyer adds. “The Sept.10, 2017, event is far from the strongest, but it is of special interest because it demonstrates the need for continual vigilance even during Solar Minimum.”
Source: Spaceweather.com



























Leave a Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.