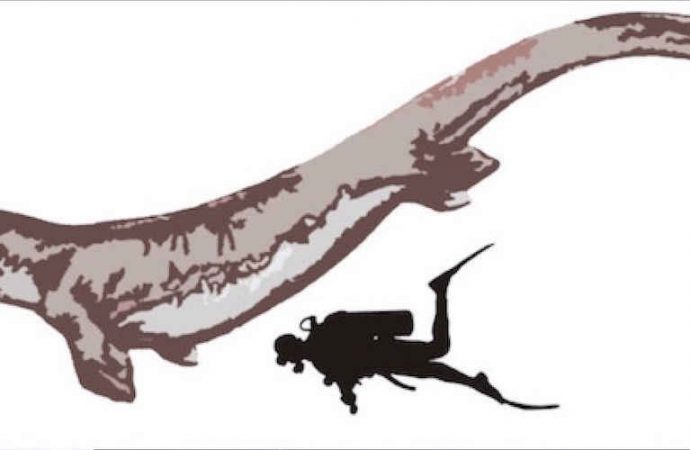
About 66 million years ago, an ancient sea monster the height of a five-story office building once gnashed its sharp teeth as it swam around the dark waters of Antarctica, a new study finds.
The newfound beast, known as a mosasaur — a Cretaceous-age aquatic reptile that sped through the ancient seas using its paddle-like limbs and long tail — is only the second fossilized mosasaur skull ever found in Antarctica.
The mosasaur specimen is different enough from other known species that it qualifies for its own genus and species. Researchers named it Kaikaifilu hervei after “Kai-Kai filú,” an almighty giant reptile that owns the sea in legends from the Mapuche culture from southern Chile and Argentina. The species name honors Francisco Hervé, a world-renowned Chilean geologist and Antarctic explorer, the researchers said.
Scientists with the Chilean Paleontological Expedition discovered the mosasaur skull on Seymour Island in January 2011. The team had run into bad weather, and only during the last few days in the field, while they were mucking around in knee-deep mud, did they discover the enormous fossil, the researchers said.
Based on the skull’s anatomy and size (4 feet, or 1.2 meters, long), the reptile’s entire body stretched about 33 feet (10 m), making it the largest marine predator in the region, the researchers said.


Credit: Otero, R.A. et al, Cretaceous Research. 2016.
North versus South
It’s not uncommon to find mosasaur remains in North America, especially in the seaway that once divided the East from the West in North America. But with the exception of New Zealand, it’s relatively rare to find the giant creatures in the Southern Hemisphere, said Rodrigo Otero, a paleontologist at the University of Chile and the lead researcher on the study.
Still, K. hervei was a close relative of — and similar in size to — the North American mosasaur known as Tylosaurus, which lived about 20 million years earlier. K. hervei was also a close relative of another Antarctic mosasaur (Taniwhasaurus antarcticus), which was smaller, with a skull about 2.3 feet (0.7 m) in length, and lived about 5 million years before K. hervei did, the researchers said.
What’s more, other researchers have found an array of other isolated mosasaur teethin the rocks of Antarctica. Mosasaurs have multiple types of teeth (a condition called heterodonty), meaning that differently shaped teeth might belong to the same mosasaur species. Thus, researchers will need to be careful not to overestimate the number of species as they review the discovered teeth, the researchers said.
Warm Antarctic
Although Antarctica is now a frigid continent, it was warmer during the dinosaur age, the researchers said. A slew of animals swam in the region’s waters, giving K. hervei a smorgasbord of contemporaries to dine on, they said.
For instance, the plesiosaurs— mostly long-necked marine reptiles that ate plankton via filter feeding — likely would have been prime targets for K. hervei, the researchers said.
“Prior to this research, the known mosasaur remains from Antarctica provided no evidence for the presence of very large predators like Kaikaifilu, in an environment where plesiosaurs were especially abundant,” Otero said in a statement. “The new find complements one expected ecological element of the Antarctic ecosystem during the latest Cretaceous.”
Source: Live Science




























Leave a Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.