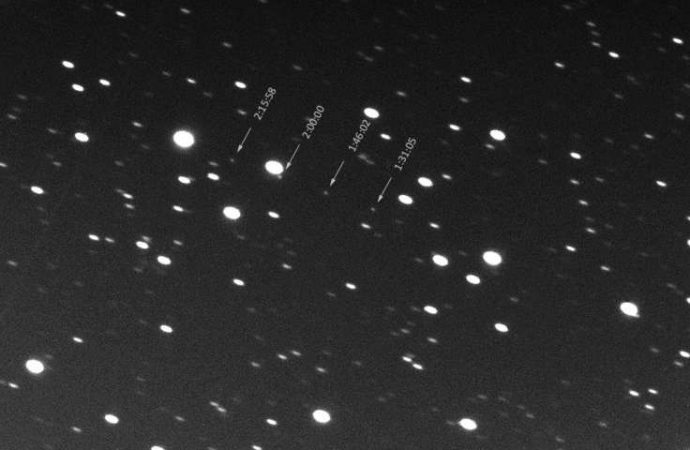
The asteroid Phaethon makes an unusual orbit around the sun, as it flies following us around it.
Discovered in 1983, the near-Earth asteroid Phaethon is an intriguing object, primarily due to its unusual orbit. Recently, an international team of astronomers has conducted a detailed study of this unique space rock, deriving a shape model that characterizes the orbit, spin state, and thermophysical parameters of the asteroid. The findings were presented in a paper published online on May 27 on arXiv.org.
Phaethon is an Apollo asteroid, though it is also suspected to be a member of the Pallas family of asteroids. It approaches the sun more closely than any other named asteroid—its perihelion is only 0.14 AU (about 21 million kilometers). The scientific community believes that this object is the parent body of the Geminid meteor shower seen on the sky every mid-December. For this reason, researchers are trying to detect any activity around this asteroid associated with dust particles being ejected from its surface. However, detecting the activity from this object has always been challenging, because of its close approaches to the sun and also due to its small elongation.
“Phaethon’s elongation is rather small, thus its light curves have small amplitudes of about 0.1 magnitude,” Josef Hanuš, the lead author of the paper describing the shape model of Phaethon, told Phys.org.
Shape modeling requires photometric data that sample various observing geometries as it is necessary to look at the asteroid from different directions. Thus, data spanning decades are usually required. Therefore, Hanuš and his team gathered a total of 55 dense-in-time light curves of Phaethon obtained between 1994 and 2015. They have also acquired their own 29 new light curves with various telescopes worldwide.
“Data from each apparition are equally important and they all contributed to the shape model determination. We used light curves obtained with nine different telescopes, and all of them were important. The largest and most impressive telescope we used was the University of Hawaii 2.2 meter telescope on Mauna Kea, both because of its great performance as well as its history. I actually observed with this telescope in September and October 2015 when Phaethon’s brightness was only 18 to 19 magnitude,” Hanuš said.
Based on these light curves, the scientists were able to derive a unique shape model of Phaethon. According to their estimates, the sidereal rotation period of this asteroid is about 3.6 hours and its size is about 5.1 km. The team also managed to measure the asteroid’s thermal inertia, geometric visible albedo and the macroscopic surface roughness.
“We contributed with reliable orbital, physical and thermophysical characterization. Thus we now know the past dynamical evolution of Phaethon’s orbit and its rotation axis direction, its size, rotation period, spin axis orientation, reflectance like the geometric visible albedo of the surface, and its thermal inertia, which corresponds to the resistance of the material to the temperature changes,” Hanuš noted.
These values presented in the new study are consistent with previous estimates.
The interest of scientists in Phaethon is now increasing, because in December 2017, it will make a close approach to the Earth at a distance of approximately 0.069 AU (about 10 million kilometers). During this event, the asteroid will be observed with multiple techniques and a large amount of data will be obtained about this intriguing space rock. The model described in the paper could be useful for planning the observations during the upcoming flyby.
“Future observing campaigns should benefit from our results since they will be useful for carefully planning them,” Hanuš concluded.
Right now, the scientists are focusing on their further studies of Phaethon—for example, they would like to reveal the true nature of the asteroid’s composition and shed more light into the proposed Phaethon-Geminid-Pallas relationship.
Source: Phys.org




























Leave a Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.